ASPCA is founded
On April 10, 1866, the American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) is founded in New York City by philanthropist and diplomat Henry Bergh, 54.
In 1863, Bergh had been appointed by President Abraham Lincoln to a diplomatic post at the Russian court of Czar Alexander II. It was there that he was horrified to witness work horses beaten by their peasant drivers. En route back to America, a June 1865 visit to the Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals in London awakened his determination to secure a charter not only to incorporate the ASPCA but to exercise the power to arrest and prosecute violators of the law.
Back in New York, Bergh pleaded on behalf of “these mute servants of mankind” at a February 8, 1866, meeting at Clinton Hall. He argued that protecting animals was an issue that crossed party lines and class boundaries. “This is a matter purely of conscience; it has no perplexing side issues,” he said. “It is a moral question in all its aspects.” The speech prompted a number of dignitaries to sign his “Declaration of the Rights of Animals.”
Bergh’s impassioned accounts of the horrors inflicted on animals convinced the New York State legislature to pass the charter incorporating the ASPCA on April 10, 1866. Nine days later, the first effective anti-cruelty law in the United States was passed, allowing the ASPCA to investigate complaints of animal cruelty and to make arrests.
Bergh was a hands-on reformer, becoming a familiar sight on the streets and in the courtrooms of New York. He regularly inspected slaughter houses, worked with police to close down dog- and rat-fighting pits and lectured in schools and to adult societies. In 1867, the ASPCA established and operated the nation’s first ambulance for horses.
As the pioneer and innovator of the humane movement, the ASPCA quickly became the model for more than 25 other humane organizations in the United States and Canada. And by the time Bergh died in 1888, 37 of the 38 states in the Union had passed anti-cruelty laws.
Bergh’s dramatic street rescues of mistreated horses and livestock served as a model for those trying to protect abused children. After Mary Ellen McCormack, 9, was found tied to a bed and brutally beaten by her foster parents in 1874, activists founded the New York Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Children. Bergh served as one of the group’s first vice presidents.
MEXICO
1919
Revolutionary leader Emiliano Zapata assassinated in Mexico
Emiliano Zapata, a leader of peasants and indigenous people during the Mexican Revolution, is ambushed and shot to death in Morelos by government forces. Born a peasant in 1879, Zapata was forced into the Mexican army in 1908 following his attempt to recover village lands taken.
WORLD WAR II
1942
Bataan Death March begins
The day after the surrender of the main Philippine island of Luzon to the Japanese, the 75,000 Filipino and American troops captured on the Bataan Peninsula begin a forced march to a prison camp near Cabanatuan. During this infamous trek, known as the “Bataan Death March.”
ART, LITERATURE, AND FILM HISTORY
1906
O. Henry’s “The Gift of the Magi” is published
O. Henry’s second short story collection, The Four Million, is published. The collection includes one of his most beloved stories, "The Gift of the Magi," about a poor but devoted couple who each sacrifice their most valuable possession to buy a gift for the other.
ART, LITERATURE, AND FILM HISTORY
1970
Paul McCartney announces the breakup of the Beatles
The legendary rock band the Beatles spent the better part of three years breaking up in the late 1960s, and even longer than that hashing out who did what and why. And by the spring of 1970, there was little more than a tangled set of business relationships keeping the group together.
ART, LITERATURE, AND FILM HISTORY
1953
First color 3-D film opens
On April 10, 1953, the horror film The House of Wax, starring Vincent Price, opens at New York’s Paramount Theater. Released by Warner Brothers, it was the first movie from a major motion-picture studio to be shot using the three-dimensional, or stereoscopic, film process and one the first horror films to be shot in color.
NATURAL DISASTERS & ENVIRONMENT
1963
Atomic submarine USS Thresher sinks in the Atlantic, killing all on board
On April 10, 1963, the USS Thresher, an atomic submarine, sinks in the Atlantic Ocean, killing the entire crew. One hundred and twenty-nine sailors and civilians were lost when the sub unexpectedly plunged to the sea floor roughly 300 miles off the coast of New England.
CRIME
1834
A torture chamber is uncovered by arson
On April 10, 1834, a fire at the LaLaurie mansion in New Orleans, Louisiana, leads to the discovery of a torture chamber where enslaved workers are routinely brutalized by Delphine LaLaurie. Rescuers found a 70-year-old black woman trapped in the kitchen during the fire because she was chained up while LaLaurie was busy saving her furniture.
COLD WAR
1971
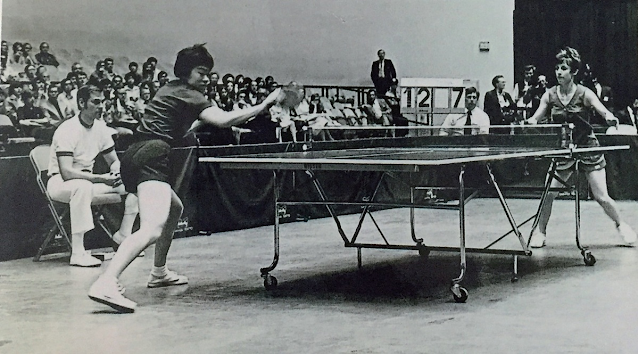
U.S. table tennis team visits communist China
The U.S. table tennis team begins a weeklong visit to the People’s Republic of China (PRC) at the invitation of China’s communist government. The well-publicized trip was part of the PRC’s attempt to build closer diplomatic relations with the United States, and was the beginning of what some pundits in the United States referred to as “ping-pong diplomacy.”
CIVIL WAR
1865
After surrendering to Union, General Lee gives final address to troops
One day after surrendering to Union General Ulysses S. Grant, Confederate General Robert E. Lee addresses his army for the last time. “After four years of arduous service, marked by unsurpassed courage and fortitude, the Army of Northern Virginia has been compelled to yield to overwhelming numbers and resources.
AMERICAN REVOLUTION
1778
Revolutionary War Commander John Paul Jones sets out to raid British ships
On April 10, 1778, Commander John Paul Jones and his crew of 140 men aboard the USS Ranger set sail from the naval port at Brest, France, and head toward the Irish Sea to begin raids on British warships. This was the first mission of its kind during the Revolutionary War.
WORLD WAR II
1941
Croatia declares independence
On April 10, 1941, the German and Italian invaders of Yugoslavia set up the Independent State of Croatia (also including Bosnia and Herzegovina) and place nationalist leader Ante Pavelic’s Ustase, pro-fascist insurgents, in control of what is no more than a puppet Axis regime.











Comments
Post a Comment